|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Your IP is:
216.73.216.121
Server uptime:
153d 5h 48m
Last site update:
09 Mar. 2011
Website visited:
387712 times
|
|
|
 |  | The ZeeRO mobile robot is a two wheels differential drive vehicle.
The two servo-motors are directly controlled by a component of the central processing unit (the Brainstem GP 1.0).
Two additional servo-motors compose a pan-tilt unit for the CMUcam2 video camera, controlled directly by the
CMUcam2's SX52 microcontroller (up to 5 servomotors can be controlled).
Figure 1 shows the general architecture of the ZeeRO mobile robot, with its main modules:
navigation, sensors, processing and communication.
Communication is handled via Bluetooth by a unit of the central processing system.
The sensor system is composed of infrared sensors (Sharp GP2D02), ultrasonic sensors (Devantech SRF08 and SRF10),
a CMUcam2 video camera and a pyroelectric sensor (Eltec 442-3).
Figure 2 shows the connections between the main elements of the central processing unit.
The Waysmall Gumstix is a ubiquitous device, powered by Intel's PXA255 XScale processor, running at 400Mhz.
In our architecture, it provides the high level processing layer while Brainstem GP1.0 and Brainstem Moto1.0 represent the low level one.
A big advantage on using Gumstix is that it is powered by the Linux operating system,
making it easy to deploy and develop free open source projects. The Waysmall offers two RS232 (miniDIN-8) interfaces,
as well as an USB client one. We used the serial interfaces to connect the Brainstem network (see figure 4) and the CMUcam2 video camera.
Besides the 4MB of flash memory on the Gumstix, the user has the possibility to add additional storage space through the Waysmall SD/MMC card reader (see figure 3).
Gumstix is also equipped with wireless communication capabilities, kudos to the Infineon ROK104001 Bluetooth chipset.

Figure 3. Waysmall Gumstix
The Brainstem GP1.0 is built around a 40MHz RISC processor. It provides 5 10bit analog/digital input channels, 5 digital I/O lines, an I2C interface, 4 servomotor outputs, an IR port, a RS232 serial port, and a power supply connection. The Brainstem Moto1.0 is also built around a 40MHz RISC processor. It provides 2 PWM controlled channels, 1 analog/digital (10bit) input channel, 1 digital I/O channel, an I2C interface, a RS232 serial port, and a H-bridge connector.
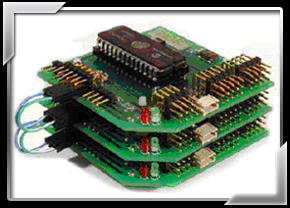
Figure 4. Brainstem GP1.0
For the ZeeRO mobile robot, the Brainstem network comprises one GP module and one Moto module, this approach providing several advantages:
- support for communication between the modules;
- only one serial connector is used to interface the network with the higher level processing units;
- only one power supply is used by the network, the power for the Moto module being supplied via the GP module.
The first prototype of the newly designed robotic architecture was finished in May 2005. As previously presented, the ZeeRO mobile robot has a variety of sensing capabilities, therefore allowing a wide range of navigation algorithms to be developed.

|

|

|
Picture 1 [1024x768]
|
Blob Follower [39Mb][avi]
|
| Picture 2 [1024x768]
|
Human Finder [22Mb][avi]
|
| Picture 3 [1024x768]
|
|
| Picture 4 [1024x768]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|